Autonomous Exploration for Shape Reconstruction and Measurement via Informative Contact-Guided Planning (AESRM)
Abstract
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are widely used for high-precision inspection of industrial parts, particularly in scenarios where visual systems are ineffective or cost-prohibitive. However, conventional CMMs rely on CAD model priors and user-defined probing paths, which limit their applicability and efficiency in measuring freeform parts. To overcome these limitations, we present a fully autonomous, CAD model-free, tactile-based framework that enables dense 3D shape reconstruction to facilitate subsequent measurements. Our approach leverages a dual Gaussian Process Implicit Surface architecture, termed Exploration-Reconstruction GPIS (ER-GPIS), which enables both high-fidelity shape reconstruction and uncertainty estimation on the object’s surface. A hybrid exploration motion planner is then employed to adaptively sample surface geometries by integrating local surface exploration, global exploration, and contact recovery policies for robust shape estimation. Extensive real-world experiments demonstrate that the proposed method effectively reconstructs object geometries across diverse shapes, highlighting its ability to autonomously reconstruct and measure both surfaces and internal features without relying on CAD model priors.
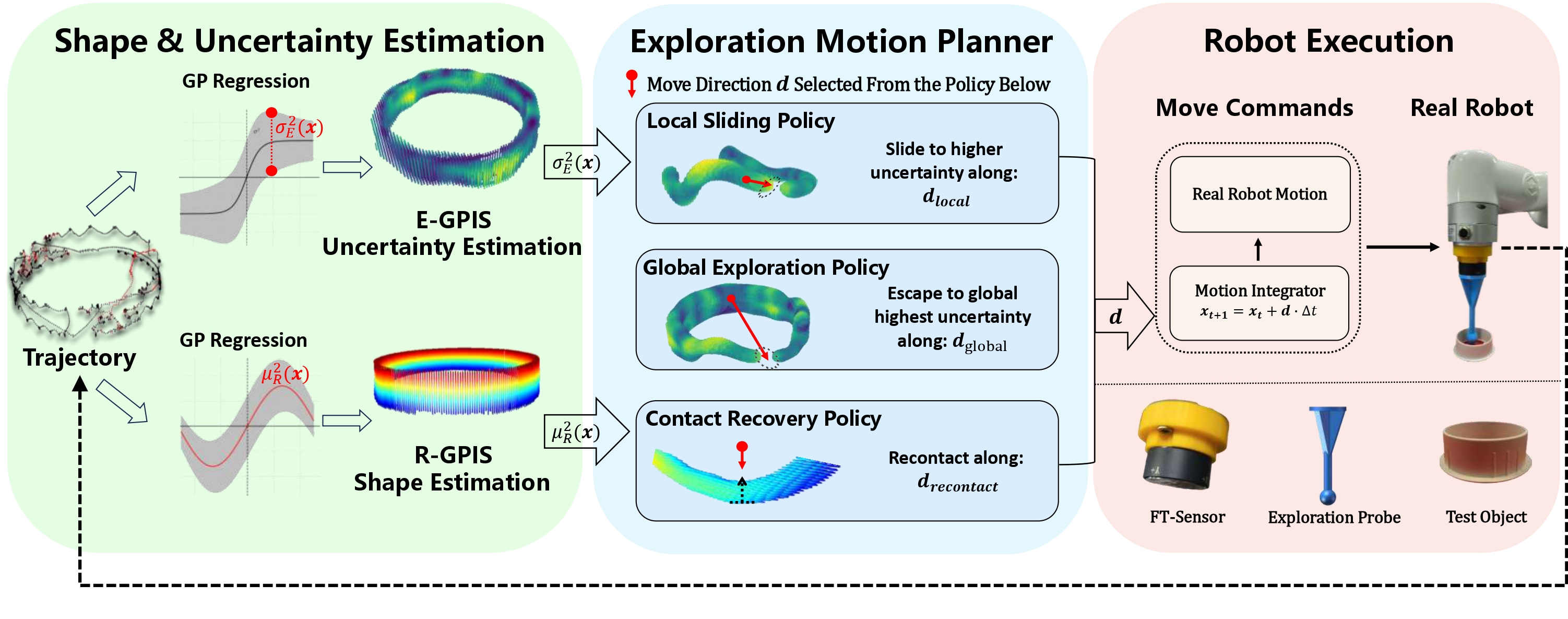
Pipeline
Overview of the proposed technical pipeline. The system consists of three interconnected modules: (1) Shape & Uncertainty Estimation: Two Gaussian Process models are employed. E-GPIS estimates uncertainty \( \sigma_E^2(x) \) to guide exploration, while R-GPIS estimates \( \mu_R^2(x) \) for shape reconstruction. (2) Exploration Motion Planner: The motion direction \( \mathbf{d} \) is calculated from either of three policies to guide exploration: Local Sliding Policy slides toward higher local uncertainty \( \mathbf{d}_{\text{local}} \); Global Exploration Policy redirects toward highest global uncertain regions \( \mathbf{d}_{\text{global}} \); Contact Recovery Policy restores contact along surface normals \( \mathbf{d}_{\text{recontact}} \). (3) Robot Execution: The robot system includes an FT-sensor and an exploration probe. The selected direction is executed on this robot system via a low-level controller.
Reconstructed Results
Explore different objects, obtain trajectories, and reconstruct the results.
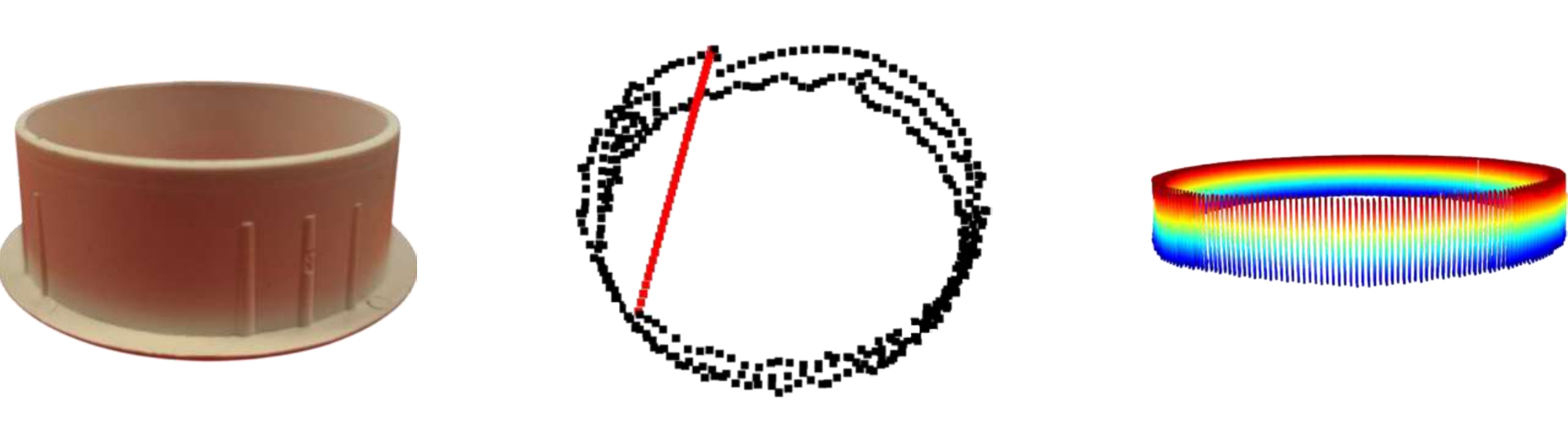
Cylindrical
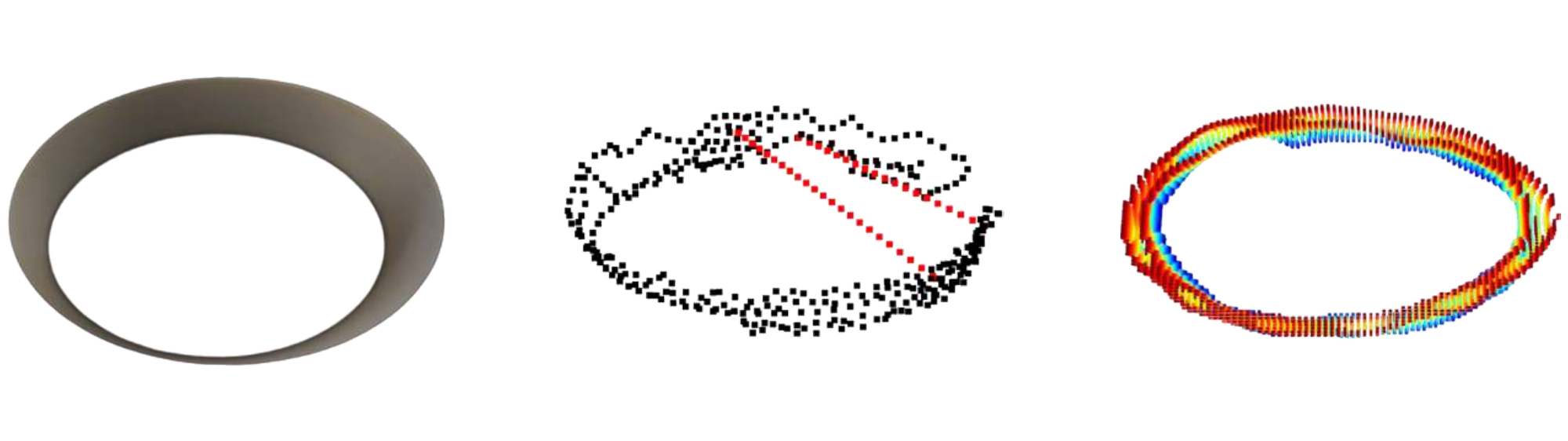
Inclined
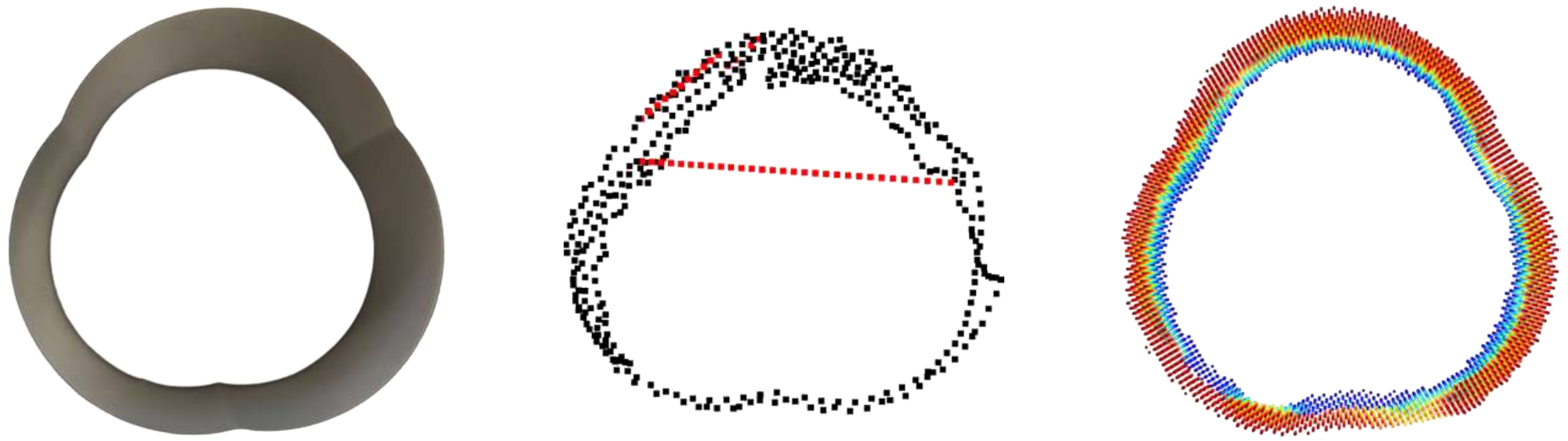
Irregular
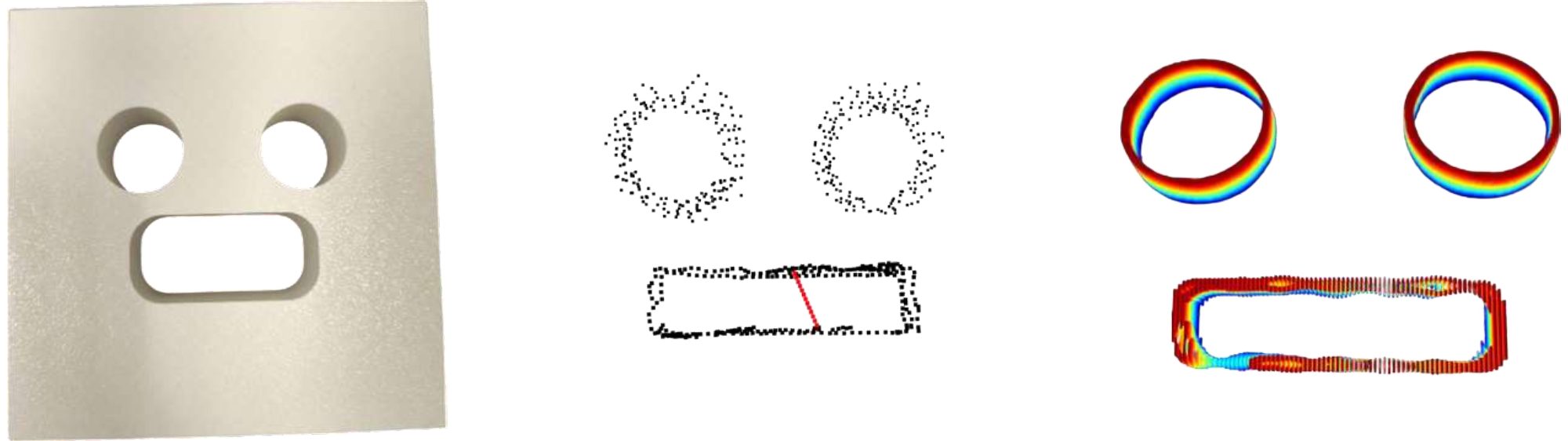
Emoji-shaped
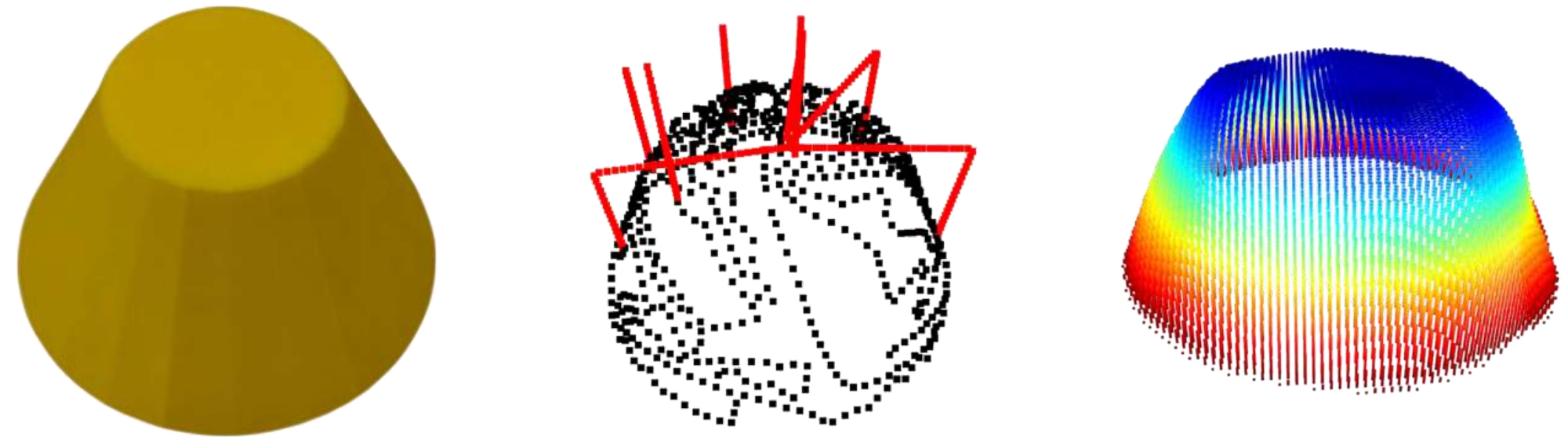
Conical
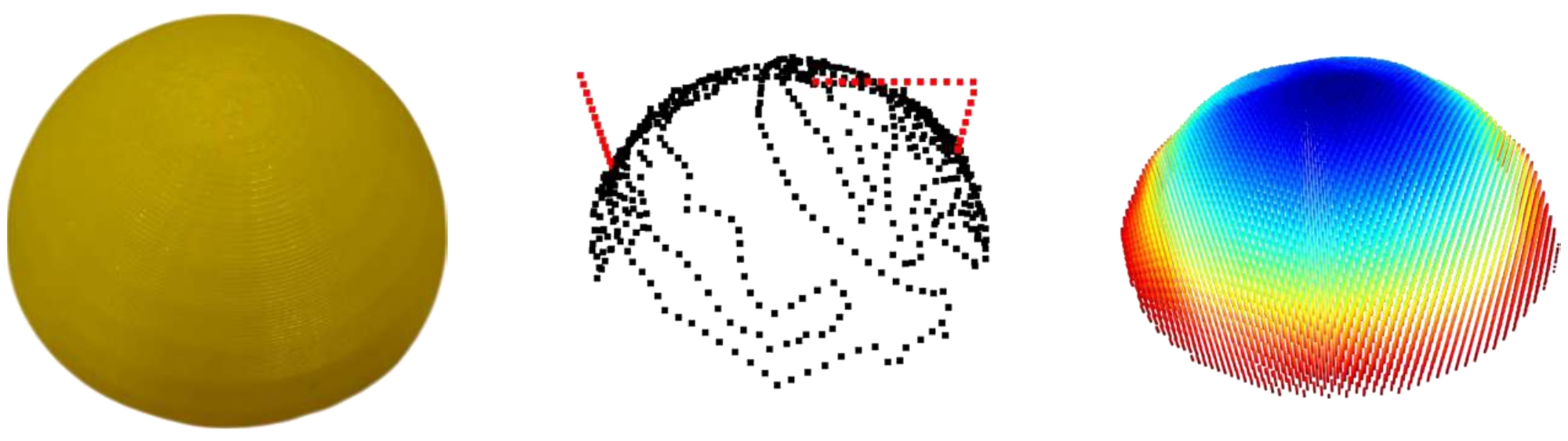
Hemispherica
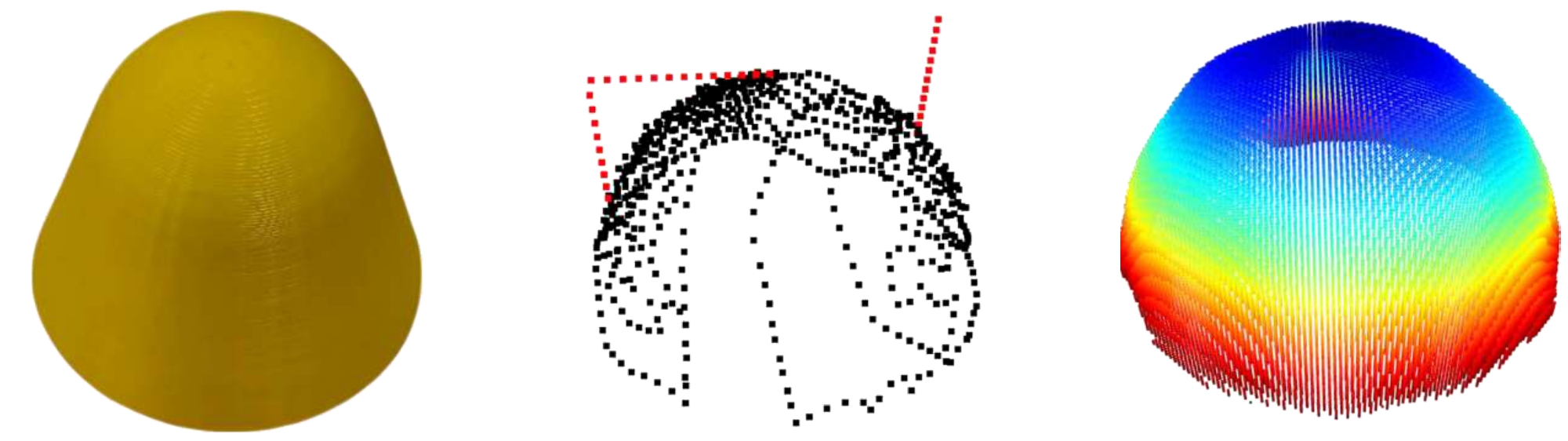
Dome
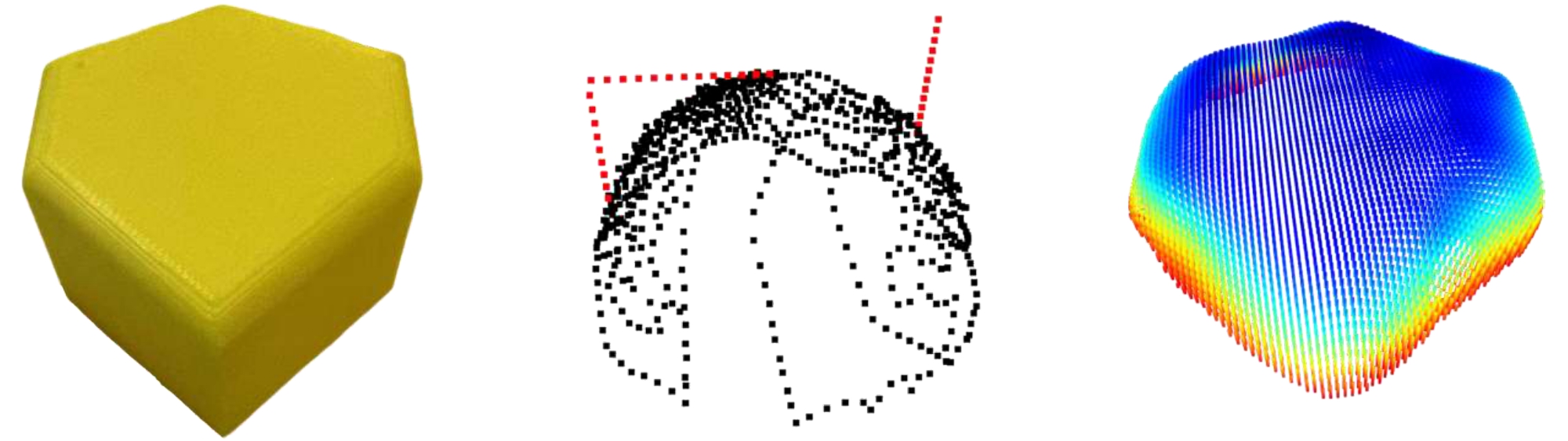
Polygona
Reconstruction Accuracy
| Object | OBJ.1 (cylindrical) | OBJ.2 (inclined) | OBJ.3 (irregular) | OBJ.4 (emoji) | OBJ.5 (conical) | OBJ.6 (hemispherical) | OBJ.7 (domed) | OBJ.8 (polygonal) | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD (mm2) | 3.02 | 4.50 | 4.35 | 8.53 | 7.54 | 2.86 | 3.01 | 8.80 | 5.270 |
| RMSD (mm) | 0.85 | 1.10 | 5.17 | 2.81 | 1.94 | 1.19 | 1.22 | 2.09 | 2.046 |
| Dia. Err. (mm) | 3.81 | 2.10 | 4.89 | 5.29 | 2.12 | 0.97 | 1.08 | 2.66 | 2.865 |
| Run Time (min) | 6m18s | 6m03s | 6m15s | 8m39s | 25m00s | 14m19s | 18m15s | 21m39s | -- |
| GPU Memory (GB) | 3.6 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 12.1 | 7.4 | 7.5 | 8.1 | -- |
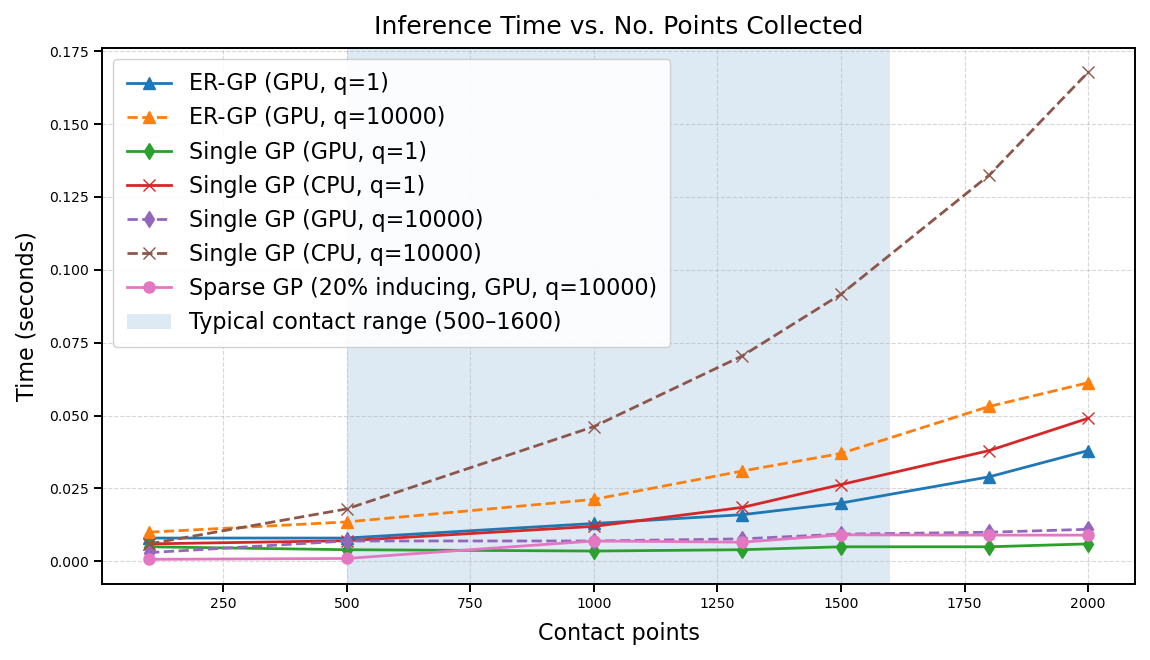
Time cost of different GPs
BibTeX
@ARTICLE{11278598,
author={Zhao, Feiyu and Xiao, Chenxi},
journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
title={Autonomous Exploration for Shape Reconstruction and Measurement via Informative Contact-Guided Planning},
year={2026},
volume={11},
number={2},
pages={1250-1257},
doi={10.1109/LRA.2025.3641100}}
}